Liability: Definition, Types, Example, and Assets vs Liabilities

Contingent liabilities are potential liabilities that depend on the outcome of future events. For example contingent liabilities can Food Truck Accounting become current or long-term if realized. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.

What are liability accounts?
In very specific contract liabilities, liability accounts failure to pay on the installment date will produce penalties, and such penalties can also be considered a cost of having liabilities. Balance sheet presentations differ, but the concept remains the same. Some businesses prefer the account-form balance sheet, wherein assets are presented on the left side while liabilities and equity are presented on the right (see highlighted part). They are current liabilities, long-term liabilities and contingent liabilities. Current and long-term liabilities are going to be the most common ones that you see in your business.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
A liability is generally an obligation between one party and another that’s not yet completed or paid. If it is expected to be settled in the short-term (normally within 1 year), then it is a current liability. In the case of non-payment creditors has the authority to claim or confiscate the company’s assets. Even in the case of bankruptcy, creditors have the first claim on assets. This can either be raised through equity (Issuance of shares on the stock exchange) or debt (Obtained from banks or issuance of bonds).

Measurement of Liabilities
It is unusual that the amount shown for each of these accounts is the same. Interest Expense will be closed automatically at the end of each accounting year and will start the next accounting year with a $0 balance. Revenue/income accounts and capital accounts are classified as income or revenue account , while proprietorship, Partnership , trusts, unincorporated organizations etc. The debit and credit sides of accounts can both go up or down depending on the nature of transactions recorded in such accounts. For example, the amount of capital of Mr. John on the first day of the accounting period will be shown on the credit side of John’s Capital Account. Any decrease is recorded on the debit side of the respective capital account.
- The accounts for non-operating expenses and losses will have debit balances since they cause stockholders’ equity to decrease.
- The income statement accounts are also known as temporary accounts since the balances in these accounts will be closed at the end of the accounting year.
- If that is not certain, then an expense should be reported in the accounting period in which its cost expires or is used up.
- If more goods are bought from United Traders (thereby incurring an additional liability to United Traders), an entry would be made on the credit side of United Traders Account.
- Liabilities are best described as debts that don’t directly generate revenue, though they share a close relationship.
- Depreciation allocates the asset’s cost (minus any expected salvage value) to expense in the accounting periods in which the asset is used.
- Perhaps the timeline/checklist will indicate that JE33 must be submitted by the accounts payable clerk six days after each month ends.
- For example, if you’re figuring out one year’s current liabilities, you would factor in 12 mortgage payments.
- But there are other calculations that involve liabilities that you might perform—to analyze them and make sure your cash isn’t constantly tied up in paying off your debts.
- Let’s assume that Servco Company receives $4,000 on December 10 for services it will provide at a later date.
- In the case of non-payment creditors has the authority to claim or confiscate the company’s assets.
But there are other calculations that involve liabilities that you might perform—to analyze them and make sure your cash isn’t constantly tied up in paying off your debts. Many first-time entrepreneurs are wary of debt, but for a business, having manageable debt has benefits as long as you don’t exceed your limits. Read on to learn more about the importance of liabilities, the different types, and their placement on your balance sheet.
Descriptions of asset accounts
A formal written promise to pay interest every six months and the principal amount at maturity. The general guidelines and principles, standards and detailed rules, plus industry practices that exist for financial reporting. When inventory items are acquired or produced at varying costs, the company will need to make an assumption on how to flow the changing costs. Again, a company should have internal controls to ensure that only legitimate payments are processed.
Do you own a business?
- The timeline will indicate what needs to be done and the sequence in which things need to occur.
- Noncurrent liabilitiesThese are also referred to as long-term liabilities.
- Examples of contingent liabilities are the outcome of a lawsuit, a government investigation, or the threat of expropriation.
- To reduce the normal credit balance in stockholders’ equity accounts, a debit will be needed.
- Otherwise, you will need to manually add your liabilities up in your spreadsheet or the software of your choice.
- One of the few examples of a contra liability account is the discount on bonds payable (or notes payable) account.
Unlock the potential of liability account with the comprehensive Lark glossary guide. A sorting of a company’s accounts receivables by the age of the receivables. The $1,500 balance in Wages Payable is the true amount not yet paid to employees for their work through December 31.
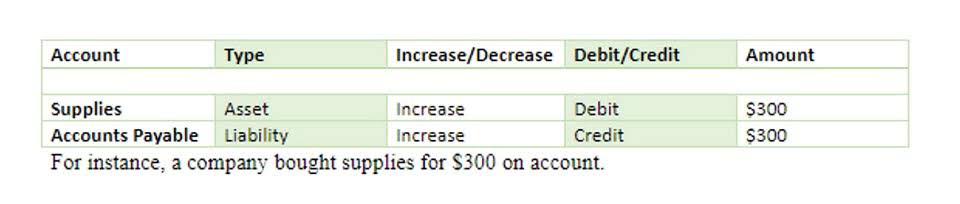
When this happens, you can reasonably estimate the amount of the resulting liability. These can play a critical role in the long-term financing of your business and your long-term solvency. If you’re unable to repay any of your non-current liabilities when they’re due, your business could end up in a solvency crisis. Usually, bookkeeping you would receive some type of invoice from a vendor or organization to pay off any debts. Simply put, liabilities are any current debts that your business owes.
Bookkeeping
The $13,420 of Wages Expense is the total of the wages used by the company through December 31. The Wages Payable amount will be carried forward to the next accounting year. The Wages Expense amount will be zeroed out so that the next accounting year begins with a $0 balance.
